Lib Dems back new policy on Democracy and Public Debate
At our recent conference the Party backed a new policy paper on Democracy and Public Debate.
This is what I said in support
Conference, As we saw from the debate last Autumn, policy on public debate and free speech is a difficult one to get right, particularly online. We have to make sure as a party that we find the proper balance between the right not to experience harm online and the right to freedom of expression.
I admit that none of us are going to agree with every single word of a policy document when the digital world is moving so fast but this is a good motion and we need to make decisions.
I spent 6 months of last year on the Joint Scrutiny Committee looking in detail at the Government’s flawed proposals for the regulation of online harms in the draft Online Safety Bill. We heard evidence from a great number of witnesses about the grievous harms such as revenge porn, cyberflashing, trolling, encouragement to suicide and racism, being experienced online, in particular by children, and those with protected characteristics.
We also heard about the potentially dangerous impact of online platforms on our democracy in the way their algorithms and business models target messages- often extreme-using our own behavioural data.
Frances Haugen-the brave former Facebook now Meta employee in particular gave us a vital insight into the threats to our democracy from online mis and dis-information and the platforms’ failure to take adequate action.
The January 6th Riot at the Capitol in Washington was fuelled by Social Media. We now know the reality of Russian interference in Presidential elections and the Brexit Referendum via opaque social media accounts.
People should have the same rights online as they have offline and we must also recognize the unique dangers that online access sometimes poses.
The Online Safety Bill is due to be published this coming week. The Elections Bill is going through Parliament. We have new digital competition law coming down the track. If we pass this motion today it will give us a distinctive Liberal Democrat approach that we can be proud of.
Our Digital Bill of Rights will set out the principles of the approach. In particular : the right to free expression and participation online without being subject to harassment and abuse which should underpin our Party and Society.
We must regulate so we ensure platforms comply with these principles, are audited for their policies and processes in terms of treatment of users and dissemination of illegal content monitored on how they respond to infringement and sanctioned for failure, with the Communications Court as a backstop.
Media and digital literacy too, so strongly emphasized by the Democracy and Public Debate paper, is vital too. We need, as it says, to combat misinformation with critical thinking.
Conference this motion combines principles, regulation and education in the right proportion. Please back it overwhelmingly.
To Save Democracy We Must Tackle Dis- and Misinformation Online
Recently the House of Lords debated the Report "Digital Technology and the Resurrection of Trust" produced by the Democracy and Digital Technologies Select Committee chaired by Lord David Puttnam, now sadly retired from the House of Lords
This is an edited version of the speech I gave winding up the debate

My Lords, this has been an inspiring debate. Events in Ukraine should make us all cherish our democracy in Britain and reinforce our determination to reinforce democratic values across the world. Nothing can compare with the suffering of the Ukrainian people in the defence of their democracy: they are a shining example to us all.
It is regrettable that we are debating this excellent report, which is still highly topical, nearly two years after it was published. I, like all of us who have spoken in this debate, very much miss Lord Puttnam leading the charge on the issues so important to him, and with which his valedictory lecture last October dealt so brilliantly. We also owe a big debt of gratitude to the noble Lord, Lord Lipsey, for stepping in and for his masterful introduction. It is good to see so many members of the committee participating today.
As the noble Lord, Lord Lipsey, says, what seemed controversial then has become commonplace today. Some of the recommendations of the committee are already in the pipeline, but we need to give far more attention to the other recommendations that are not in the pipeline. Given the crossover with many aspects of the report of the Joint Committee on the Draft Online Safety Bill, I am particularly pleased to be taking part in this debate today.
In a piecemfour years ago, US tech journalist Dylan Matthews wrote:
“The internet was supposed to save democracy… How could we have gotten this so wrong?”
He wrote this in the light of allegedmanipulation by Russia both in the US presidential elections and in the Brexit vote, with the aid of Cambridge Analytica, which used data collected online from millions of personal Facebook accounts, targeting individuals with specific misinformation. As the noble Baroness, Lady Morris, said, we were too slow to see the risks. As the noble Lord, Lord Stevenson, said, who doubts this activity now?
In the intervening years, the power of viral disinformation on social media has become even clearer. The long-delayed report on Russian interference, by the Intelligence and Security Committee in July 2020, said:
“The UK is clearly a target for Russia’s disinformation campaigns and political influence operations and must therefore equip itself to counter such efforts.”
We also had the riots at the Capitol in Washington DC on 6 January 2021, mentioned by the noble Lord, Lord Harris. An investigation by ProPublica and the Washington Post found that Facebook groups swelled —with at least 650,000 posts attacking the legitimacy of Joe Biden’s victory—between election day and the 6 January riot, with many calling for executions or other political violence.
We have had former Facebook—now Meta—employee Frances Haugen’s damning testimony, mentioned by the noble Baroness, Lady Kidron, and the noble Lord, Lord Mitchell, to the USA Senate and our own Joint Committee on the Draft Online Safety Bill, on which I sat. She accused the company of putting
“astronomical profits before people.”
Most of us need little convincing that things have gone badly wrong somewhere, and in 2022, after Covid lockdown, the situation seems worse. But as the report of the Democracy and Digital Technologies Committee says, we must look at the roots of the problem and the accountabilities involved. It is all about the power of the algorithm and data, as the noble Lords, Lord Stevenson and Lord Mitchell, said.
We are being targeted with our own data. Online political microtargeting is used to alter how we vote, especially with misinformation. xtreme content is amplified as part of the platform business model. Outrage is encouraged. Their business models operate directly against the best interests of a democratic society. They prey on us, in that vivid phrase quoted by the noble Baroness, Lady Kidron. Lord Puttnam made the strong point in his valedictory lecture that 6 January was a wake-up call to tackling the problems with microtargeting and algorithm bias which underlie the business models of the social media platforms.
Ownership of data is increasingly concentrated in the hands of big internet brands, as we have heard from a number of noble Lords today. Metcalfe’s law of networks has led to enormous and growing power for social media.
What should the consequences be for social media? How can we prevent these harms to democracy? How can we restore trust—or resurrect it, in the words of the report? The bottom line is that we do have the power, as the noble Lords, Lord Holmes and Lord Stevenson, said. We need government regulation, and quickly. In the phrase used by Avaaz, we need to detoxify the algorithm, not only regarding hate speech, terrorism and cyberbullying but in very clear electoral regulation and action by the Competition and Markets Authority to enforce competition in the tech and data space.
We also need much greater personal control over our data and how it is used. Misinformation and disinformation are particularly hard to define, but as the committee said, if the Government decide that the Online Safety Bill is not the appropriate place to do so, then it should use the Elections Bill, which is currently making its way through Parliament. Tackling societal harms caused by misinformation and disinformation is not straightforward, as our Joint Committee found, but the draft online safety Bill, as we described in our report of last December, needs to go further.
There is of course a tension with freedom of expression and as we emphasised, we must prioritise tackling specific harmful activity over restricting content.
In our Joint Committee report, we recommended safety by design requirements, such as increasing transparency and countering algorithmic power and virality; as Fair Vote says, it is a proven way to preserve free speech, while limiting free reach of content that poses societal harm at scale. For example, we heard that a simple change—introducing more friction into sharing on Facebook—would have the same effect on the spread of misinformation and disinformation as the entire third-party fact checking system.
We do not yet know what the Government’s response to these recommendations is—that may come next week—but we do have the Elections Bill in front of us. The real government reluctance is in reform of electoral law and regulation of digital political activity. Apart from the digital imprint provisions, the Bill fails to take any account of the mounting evidence and concerns about the impact on our democracy of misinformation and disinformation. The Government are yet even to adopt the Electoral Commission report of June 2018, Digital Campaigning: Increasing Transparency for Voters, which called for urgent reforms to electoral law to combat misinformation, misuse of personal data and overseas interference in elections amid concerns that British democracy may be under threat. Why are these recommendations not contained in the Elections Bill? We heard in the previous debate today about the flaws in that Bill
How prescient was the ISC in its Russia report:
“The links of the Russian elite to the UK – especially where this involves business and investment – provide access to UK companies and political figures, and thereby a means for broad Russian influence in the UK. To a certain extent, this cannot be untangled and the priority now must be to mitigate the risk and ensure that, where hostile activity is uncovered, the tools exist to tackle it at source.”
Most recently, the Committee on Standards in Public Life has made a number of other important recommendations regarding digital and social media campaigning.
But, as have heard today, this is not enough. Regulation by itself will not deal with all the issues. Even though we are facing issues that threaten democracy, we should be trying to preserve the good that the internet has done as we work to mitigate itsharm to our political system. So, as well as regulation, there needs as be—as the Democracy and Digital Technologies Committee report says—public engagement to support digital understanding at all levels of society. As several noble Lords said, digital literacy and digital skills are of huge importance, as also emphasised by the Committee’s report. We must do more than simply expect Ofcom—even under the chairmanship of the noble Lord, Lord Vaizey—to deliver a digital media strategy. This needs a whole-of-government and whole-of-society approach. We are supposed to be the cradle of democracy, yet the EU is way ahead of us in its proposals to regulate political advertising. This needs cross-governmental action and much greater action from social media platforms themselves.
At the end of the day, however,we need to look in the mirror. We deserve a better system. The Government are playing into the hands of those who wish to erode our democracy by digital means. Why are they intent on reducing the independence of the Electoral Commission? As the noble Lord, Lord Griffiths, said, trust in our democracy has been eroded by this Government—certainly by the negative response so graphically described by the noble Lord, Lord Mitchell. The Government must change tack and provide effective safeguards.
Where should facial recognition be used?
14 February 2022
Interview with
Gareth Mitchell, BBC & Stephanie Hare, Author & Lord Clement-Jones

When we think of our personal data, we often consider information like our phone number, bank details, or email address. But what about our eyes, ears, mouth, and nose? Facial recognition is increasingly being used to tag and track our individual activities, and while commonplace in unlocking personal devices like laptops and phones, certain institutions are keen to use our features for much more than mugshots. This includes the US Treasury, who last week backtracked on plans for mandatory facial verification for people logging their tax returns. So why are some people wary of firms having their faces on file? Robert Spencer finds out more...
Robert - It's a question that appears time and time again. How comfortable are we as a society with facial recognition? As unlocking your phone shows, in some respects the answer is clear, but when it comes to having your face scanned as you walk down the street, the issue becomes more murky.
Gareth - It's a biometric identifier. That means using aspects of your body for identification. The issue is that all of us are walking around in public showing our faces, meaning that anybody with a scanner, if they want to can mount a camera, and use an algorithm to identify us. We don't have any control over who is using our face as the identifier.
Robert - That's Gareth Mitchell who presents Digital Planet on the BBC world service. This lack of control and consent is key to one of the central paradoxes in the discussion around facial recognition. It speaks to the differences in technologies involved as Stephanie Hare explains in her new book, Technology Is Not Neutral: A Short Guide to Technology Ethics.
Stephanie - There are different types of facial recognition technology. So let's start with facial verification. That's the kind that you would use to unlock your own smartphone. That's not a very high risk use of facial recognition technology because the biometric never leaves your phone. A higher risk example is going to be when the police are using live facial recognition technology to identify people in a crowd. This might be high risk because it can have a chilling effect on free speech. If people fear that when they're going to these protests, they're being scanned by the police.
Robert - But it's not just about giving consent and having control of your biometrics. The algorithms themselves are large complex computer programs, often hidden behind company secrets. And it turns out, they aren't always as accurate as we'd like.
Stephanie - It doesn't work as well on people with darker skin. It works particularly poorly on women with darker skin, but it can also be a problem with children, with trans people and with elderly people.
Robert - The fix though might not be as simple as it seems.
Gareth - In order for the algorithms to get better at recognizing a whole diversity of faces, that would mean training those algorithms on more and more faces. And so opponents would say, well, that just adds to the problem. One problem is the algorithms are not very good at identifying a particular group of people. So let's just go and get loads of profiles of these kinds of people and put them into our databases. Well, then you scanned even more faces you've potentially compromised more people's privacy and that's made the problem even worse.
Robert - Police forces around the UK also disagree on the use of the technology known as live facial recognition. The Met uses facial recognition to find offenders on watchlists, but Scottish police have halted its use.
Stephanie - Right now, our experience of this technology who's using it and how it's even discussed in law differs depending on your postcode.
Gareth - And another reason why facial ID has been so controversial is that some of these police forces have been rolling it out before there was a regulatory framework in effect to protect us and, if necessary, them.
Robert - This lack of legal framework also concerns Lord Clement-Jones who debated the issued last week in the house of Lords.
Lord Clement-Jones - And the general conclusion was that there was no single piece of legislation that really covered the use of live facial recognition. It's very easy to say, we need to ban this technology and I'm not quite in that camp. What I want to see, and this was the common ground, is a review. We want to see what basis there should be for legislation, we want to see how the technology performs, and then we want to be able to decide whether we should ban it or, whether there are some uses to which it could be put with the right framework.
Robert - It's hard to ignore the distinct advantages facial recognition carries. It's fast and hands free. The ability to accurately and instantly identify a fugitive in a crowd would make the world a safer place.
Gareth - There was bound to be a trade off between our liberties and our security. We should be having conversations that are diverse, where a wide range of people are coming to the table with their views and their issues.
Stephanie - I would want to be hearing from scientists, the people who manufactured this tech, from the military, from the police, from medical professionals, from civil liberties groups. And I think it's the first step on a long journey that we have to have in the United Kingdom.
Robert - Lord Clement-Jones is optimistic.
Lord Clement-Jones - The public ought to take away from this debate, that there are a great many parliamentarians concerned about the use of new technology without proper oversight. But they should put pressure on their own MPs, to say, well, what is happening much more seriously.
Robert - It's clear then that we need to have this discussion sooner rather than later. In the meantime, though, I'm going to keep using my face to unlock my phone. I'm not sure where the line in the sand is, but for me, it's a bit past this level of convenience.
New Surveillance Code Incompatible with Human Rights
Recently the Government Introduced a revised Surveillance Camera Code of Practice which it claims make the police's use of live facial recognition compliant with the Bridges Case. This is my my speech on the regret motion I tabled in response with very helpful support from Liberty.
That this House regrets the Surveillance Camera Code of Practice because (1) it does not constitute a legitimate legal or ethical framework for the police’s use of facial recognition technology, and (2) it is incompatible with human rights requirements surrounding such technology.
My Lords, I have raised the subject of live facial recognition many times in this House and elsewhere, most recently last November, in connection with its deployment in schools. Following an incredibly brief consultation exercise, timed to coincide with the height of the summer holidays last year, the Government laid an updated Surveillance Camera Code of Practice, pursuant to the Protection of Freedoms Act 2012, before both Houses on 16 November last year, which came into effect on 12 January 2022.
The subject matter of this code is of great importance. The last Surveillance Camera Commissioner did a survey shortly before stepping down, and found that there are over 6,000 systems and 80,000 cameras in operation across 183 local authorities. The UK is now the most camera-surveilled country in the western world. According to recently published statistics, London remains the third most surveilled city in the world, with 73 surveillance cameras for every 1,000 people. We are also faced with a rising tide of the use of live facial recognition for surveillance purposes.
Let me briefly give a snapshot of the key arguments why this code is insufficient as a legitimate legal or ethical framework for the police’s use of facial recognition technology and is incompatible with human rights requirements surrounding such technology. The Home Office has explained that changes were made mainly to reflect developments since the code was first published, including changes introduced by legislation such as the Data Protection Act 2018 and those necessitated by the successful appeal of Councillor Ed Bridges in the Court of Appeal judgment on police use of live facial recognition issued in August 2020, which ruled that that South Wales Police’s use of AFR—automated facial recognition—had not in fact been in accordance with the law on several grounds, including in relation to certain convention rights, data protection legislation and the public sector equality duty.
During the fifth day in Committee on the Police, Crime, Sentencing and Courts Bill last November, the noble Baroness, Lady Williams of Trafford, the Minister, described those who know about the Bridges case as “geeks”. I am afraid that does not minimise its importance to those who want to see proper regulation of live facial recognition. In particular, the Court of Appeal held in Bridges that South Wales Police’s use of facial recognition constituted an unlawful breach of Article 8—the right to privacy—as it was not in accordance with law. Crucially, the Court of Appeal demanded that certain bare minimum safeguards were required for the question of lawfulness to even be considered.
The previous surveillance code of practice failed to provide such a basis. This, the updated version, still fails to meet the necessary standards, as the code allows wide discretion to individual police forces to develop their own policies in respect of facial recognition deployments, including the categories of people included on a watch-list and the criteria used to determine when to deploy. There are but four passing references to facial recognition in the code itself. This scant guidance cannot be considered a suitable regulatory framework for the use of facial recognition.
There is, in fact, no reference to facial recognition in the Protection of Freedoms Act 2012 itself or indeed in any other UK statute. There has been no proper democratic scrutiny over the code and there remains no explicit basis for the use of live facial recognition by police forces in the UK. The forthcoming College of Policing guidance will not satisfy that test either.
There are numerous other threats to human rights that the use of facial recognition technology poses. To the extent that it involves indiscriminately scanning, mapping and checking the identity of every person within the camera’s range—using their deeply sensitive biometric data—LFR is an enormous interference with the right to privacy under Article 8 of the ECHR. A “false match” occurs where someone is stopped following a facial recognition match but is not, in fact, the person included on the watch-list. In the event of a false match, a person attempting to go about their everyday life is subject to an invasive stop and may be required to show identification, account for themselves and even be searched under other police powers. These privacy concerns cannot be addressed by simply requiring the police to delete images captured of passers-by or by improving the accuracy of the technology.
The ECHR requires that any interference with the Article 10 right to freedom of expression or the Article 11 right to free association is in accordance with law and both necessary and proportionate. The use of facial recognition technology can be highly intimidating. If we know our faces are being scanned by police and that we are being monitored when using public spaces, we are more likely to change our behaviour and be influenced on where we go and who we choose to associate with.
Article 14 of the ECHR ensures that no one is denied their rights because of their gender, age, race, religion or beliefs, sexual orientation, disability or any other characteristic. Police use of facial recognition gives rise to two distinct discrimination issues: bias inherent in the technology itself and the use of the technology in a discriminatory way.
Liberty has raised concerns regarding the racial and socioeconomic dimensions of police trial deployments thus far—for example, at Notting Hill Carnival for two years running as well as twice in the London Borough of Newham. The disproportionate use of this technology in communities against which it “underperforms” —according to its proponent’s standards—is deeply concerning.
As regards inherent bias, a range of studies have shown facial recognition technology disproportionately misidentifies women and BAME people, meaning that people from these groups are more likely to be wrongly stopped and questioned by police and to have their images retained as the result of a false match.
The Court of Appeal determined that South Wales Police had failed to meet its public sector equality duty, which requires public bodies and others carrying out public functions to have due regard to the need to eliminate discrimination. The revised code not only fails to provide any practical guidance on the public sector equality duty but, given the inherent bias within facial recognition technology, it also fails to emphasise the rigorous analysis and testing required by the public sector equality duty.
The code itself does not cover anybody other than police and local authorities, in particular Transport for London, central government and private users where there have also been concerning developments in terms of their use of police data. For example, it was revealed that the Trafford Centre in Manchester scanned the faces of every visitor for a six-month period in 2018, using watch-lists provided by Greater Manchester Police—approximately 15 million people. LFR was also used at the privately owned but publicly accessible site around King’s Cross station. Both the Met and British Transport Police had provided images for their use, despite originally denying doing so.
It is clear from the current and potential future human rights impact of facial recognition that this technology has no place on our streets. In a recent opinion, the former Information Commissioner took the view that South Wales Police had not ensured that a fair balance had been struck between the strict necessity of the processing of sensitive data and the rights of individuals.
The breadth of public concern around this issue is growing clearer by the day. Several major cities in the US have banned the use of facial recognition and the European Parliament has called for a ban on police use of facial recognition technology in public places and predictive policing. In response to the Black Lives Matter uprisings in 2020, Microsoft, IBM and Amazon announced that they would cease selling facial recognition technology to US law enforcement bodies. Facebook, aka Meta, also recently announced that it will be shutting down its facial recognition system and deleting the “face prints” of more than a billion people after concerns were raised about the technology.
In summary, it is clear that the Surveillance Camera Code of Practice is an entirely unsuitable framework to address the serious rights risk posed by the use of live facial recognition in public spaces in the UK. As I said in November in the debate on facial recognition technology in schools, the expansion of such tools is a “short cut to a widespread surveillance state.”—[Official Report, 4/11/21; col. 1404.]
Public trust is crucial. As the Biometrics and Surveillance Camera Commissioner said in a recent blog: “What we talk about in the end, is how people will need to be able to have trust and confidence in the whole ecosystem of biometrics and surveillance”.
I have on previous occasions, not least through a Private Member’s Bill, called for a moratorium on the use of LFR. In July 2019, the House of Commons Science and Technology Committee published a report entitled The Work of the Biometrics Commissioner and the Forensic Science Regulator. It repeated a call made in an earlier 2018 report that “automatic facial recognition should not be deployed until concerns over the technology’s effectiveness and potential bias have been fully resolved.” The much-respected Ada Lovelace Institute has also called for a “a voluntary moratorium by all those selling and using facial recognition technology”, which would “enable a more informed conversation with the public about limitations and appropriate safeguards.”
Rather than update toothless codes of practice to legitimise the use of new technologies like live facial recognition, the UK should have a root and branch surveillance camera review which seeks to increase accountability and protect fundamental rights. The review should investigate the novel rights impacts of these technologies, the scale of surveillance we live under and the regulations and interventions needed to uphold our rights.
We were reminded by the leader of the Opposition on Monday about what Margaret Thatcher said, and I also said this to the Minister earlier this week:
“The first duty of Government is to uphold the law. If it tries to bob and weave and duck around that duty when it’s inconvenient, if Government does that, then so will the governed and then nothing is safe—not home, not liberty, not life itself.”
It is as apposite for this debate as it was for that debate on the immigration data exemption. Is not the Home Office bobbing and weaving and ducking precisely as described by the late Lady Thatcher?
The Road to Trustworthy Use of Healthcare Data: Good Governance and a Sovereign Health Fund
I recently did a Guest blog for Future Care Capital on Data in the Health and Care Bill

https://futurecarecapital.org.uk/latest/guest-blog-lord-clement-jones-3/
The Health and Social Care Bill currently passing through Parliament potentially contains major changes to the way that our public health data will be treated with the merging of NHS Digital and NHSX with NHS England. Important amendments are needed.
All of us recognize the benefits of using health data which arises in the course of treating patients in the NHS for research that will lead to new and improved treatments for disease and for the purposes of public health and health services planning. It has in particular been of great benefit in helping to improve the treatment of COVID during the pandemic.
The introduction of Shared Care Records is a key part of this revolution. These allow staff involved in a person’s care, to access health and care records to provide better joined-up care across different parts of the health and social care system.
But increasingly the Government and, I am sad to say, agencies such as NHS Digital and NHSX seem to think that they can share patient data with private companies with barely a nod to patient consent and proper principles of data protection.
We can go back to December 2019 and the discovery by Privacy International that the Department of Health and Social Care had agreed to give free access to NHS England health data to Amazon allowing them to develop, advertise, and sell new products, applications, cloud-based services and/or distributed software.
Take the situation last year where we had what has been described as the biggest data grab in the history of the health service of GP patient data. In May, NHS Digital with minimal consultation, explanation or publicity and without publication of any data protection impact assessment (DPIA) published its plans to share patients’ primary health care data collected by GP practices giving patients just 6 weeks to opt-out.
As a result of campaigners’ efforts, including a group of Tower Hamlets GPs who refused to hand over patient data, Ministers first announced that implementation would be delayed until 1 September and then by letter to GP’s in July put the whole scheme on hold including data collection.
As a result of this bungled approach more than a million people have now opted out of NHS data-sharing.
The government have had to revise their approach and devise a simpler opt-out system and commit to the publication of a data impact assessment before data collection starts again. They have had to commit that access to GP data will only be via a Trusted Research Environment (TRE) and commit to properly thought through engagement and communications strategy.
But if we areto retain and build trust in the use of health data, we need a new governance framework.
The Government must gain society’s trust through honesty, transparency and rigorous safeguards. The individual must have the right to choose whether to share their data or not and understand how it will be used.
We need to retain NHS Digital’s statutory safe haven functions separate from NHS England and all health data must be held anonymously and accessed through an accredited data access environment, designed to cover not only the promised TRE but also where data is used for planning purposes.
The data held by the NHS must be considered as a unique source of value held for national benefit. Retaining control over our publicly generated data, particularly health data, for planning, research and innovation is vital if the UK is to maintain its position as a leading life science economy and innovator.
We need a guarantee that our health data will be used in an ethical manner, assigned its true value and used for the benefit of UK healthcare. Any proceeds from data collaborations that the Government agrees to, integral to any replacement or new trade deals, should be ring-fenced for reinvestment in the health and care system with a Sovereign Health Fund.
Those I believe are the right foundations for health data governance and, alongside other members of the Lords such Lord Hunt of Kings Heath and Baroness Cumberledge -both with enormous experience of the health service- I will be supporting and tabling amendments during the passage of the Bill to secure them.
Artificial Intelligence and Intellectual Property: incentivize human innovation and creation
Christian Gordon-Pullar and I recently responded to the Government's Consultation Paper on Artificial Intelligence and Intellectual Property: Copyright and Patents;
This is what we said;
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) becomes embedded in people’s lives, the United Kingdom (UK) is at a pivotal inflection point. The UK’s National AI Strategy rightly recognises Artificial Intelligence (AI) as the ‘fastest growing deep technology in the world, with huge potential to rewrite the rules of entire industries, drive substantial economic growth and transform all areas of life’ and estimates that AI could deliver a 10% increase in UK GDP in 2030.
The UK is, potentially, well-positioned to be a world-leader in AI, over time, as a genuine research and innovation powerhouse, a hub for global talent and a progressive regulatory and business environment. Achieving this will involve attracting, retaining and incentivising business to create, protect and locate investment efforts in the UK. The UK has the potential to gain impetus from a position of strength in AI research, enterprise and ethical regulation, and, with its recent history of support for AI, it stands among the best in the world. To attract talent, incentivise investment in AI-powered or AI-focused innovation, influence global markets and shape global governance, the nature of the Intellectual Property regime in the UK relating to AI will be crucial.
Specifically in relation to the three headline areas of focus in the Consultation Paper:

1. Copyright: Computer Generated Works
The UK is one of only a handful of countries to protect works generated by a computer where there is no human creator. The “author” of a “computer-generated work” (CGW) is defined as “the person by whom the arrangements necessary for the creation of the work are undertaken”. Protection lasts for 50 years from the date the work is made.
In the same way the owner of the literary work and the copyright subsisting in it, if it were original, would be, alternatively:
- a) the operator of an AI system (aligning its inputs and selecting its datasets and data fields); or
- b) their employer, if employed; or
- c) a third party if the operator has a contract assigning such rights outside of employment context.
To be original, a work must be an author’s or artist’s own intellectual creation, reflecting their personality (see the decisions of the EU Court of Justice in Infopaq, C-5/08, and Painer, C-145/10).
At the other end of the scale, a human who simply provides training datato an AI system and presses “analyse” is unlikely to be considered the author of the resulting work.
In this way we believe that the existing copyright legislative framework under the CDPA adequately addresses the current needs of AI developers. New entrants and disruptors can, in our opinion, work within the existing framework which adequately caters for the existing and foreseeable future.
Indeed realistic hypothetical future scenarios may well involve an AI system having access to content from global providers and creating derivative content (whether under licence or not) and doing so at great speed with little or no investment or “sweat of the brow” and, therefore it can be argued that in fact the level of protection should be reduced to be proportionate to the time effort and investment involved.
Further, we would also urge that copyright law is clarified to ensure that it is the operator (or his /her employer) of the AI system (that is, the person that guides the AI system to apply certain data or parameters and shapes the outcome) that is the copyright owner and not the owner of the AI system.
One can see a future scenario where “AI-as-a-Service” is offered whereby a content user or hirer of the AI system is allowed to apply their own rules, parameters and data/inputs to a problem whilst ‘hiring’ or using the AI system as a service (just as SaaS exists today). The operator of the AI system (not owner of the AI system ) should in that case be the first owner of the copyright in the resulting work (subject to contractual rights that may be transferred, licensed or otherwise assigned thereafter).
Ranking Options in order:
- We would therefore urge the IPO to choose Option 2 – a lesser term of copyright protection should apply e.g. 5-15 Years for AI generated Copyright works e.g. music, art etc. which, as described above, require little investment or “sweat of the brow”
- Failing 1, we would urge the IPO to choose option 0 – Make no legal change.
- Option 1, removing the protection is not a viable or desirable option in our opinion.
2. Copyright: Text and Data Mining
The Government rightly believe that that there is a need to promote and further enable AI development. This must however be balanced with a commensurate and proportionate recognition of the critical importance and value of data as raw material.
AI developers rely on high-quality data to develop reliable and innovative AI-driven inventions and applications. Licensing regimes under existing IP law are designed to cater for the needs of AI developers.
By the same token content and data-driven businesses themselves have seen a rapid increase in the use of AI technology and machine-learning, either for news summaries, data gathering efforts, translations for research and journalistic purposes or to assist organisations to save time by processing large amounts of text and other data at scale and speed. Digital technologies, including AI, are and will continue to be of critical importance to these industries, helping create content, new products and value-added services to deliver to a broad range of corporate and retail clients. Whether in news media or cross-industry research, publishers are themselves investing in AI; continued collaboration with start-ups and academia are creating tailored materials for wide populations of beneficiaries (students, academia, research organisations, and even marketers of consumer publishing products).
It is of paramount importance to balance the needs of future AI development with the legal, commercial and economic rights of data-owners and the need to incentivize new AI adoption with recognition of the rights of existing content owners.
We have however seen no evidence the existing copyright legislative framework fails to adequately address the current needs of AI developers. Moreover it is particularly important, in our view, to ensure that the development of AI is not enabled at the expense of the underlying investment by copyright and data-owners. (see endnote 1).
If the content owners of underlying data materials withhold the licensing of, or access to, such materials or attempt to price them at a level that is unfair, the answer is for Government via the Competition and Markets Authority/the new Digital Markets Unit (or indeed other regulators who form part of the Digital Regulation Cooperation Forum) to put in place competition measures to ensure there is a clear legal recourse in such situations.
In summary we do not believe that current copyright law creates a disparity between the interests of AI developers and investors and content owners. The existing copyright regime under the CDPA reflects a balance that fairly protects those investing in data creation without giving an unfair advantage to technology companies offering AI-enabled content creation services. In particular the current framework provides a balanced regime for data and text mining and we believe no changes are required at present. However, we recommend a watching brief, and that the IPO consider and take account of changes to copyright laws in other countries that may make it more attractive for AI operators to base their operations in those extraterritorial locations so that text and data mining activities, machine learning, etc. become more easily performed elsewhere or permitted with incentives not offered in UK.
Ranking Options in order:
- We would therefore urge the IPO to elect Option 0 – Make no legal change. No other option is currently justifiable given the lack of evidence of an adverse commercial environment preventing access to data or text by AI-enabled content creators. Should the Government or IPO consider that there needs to be increased access to data at lower cost, it should look at other policy levers to stimulate such uptake, such as providing tax incentives for content owners to license content, rather than reducing copyright protection.
- We also concur with industry leads who consider that forcing rightsholders to opt in to protection, as suggested in option 3 would be complicated and costly for many businesses and industries who own literally millions of works, when licensing is far simpler, and would be against the spirit of international treaties on copyright.
3. Patents:
If UK patents were to protect AI-devised inventions, how should the inventor be identified, and who should be the patent owner? What effects does this have on incentivising and rewarding AI-devised inventions?
As we described above the author and first owner of any AI-assisted or created work will be the person who creates the work or their employer if that person is an employee or or a third party if the operator has a contract assigning such rights outside of employment context
As the emphasis in copyright law suggests, creating a ‘work’ is in essence a human activity. This is given additional support by the reference to the automatic transfer of copyright from employee to employer; an AI system cannot be said to be an employee.
Similar principles in our view apply to patents as with copyright. For patentability the applicant inventor must be a ‘person’.
Authoritative guidance on how AI-created inventions fit into this scheme, where no human inventor is mentioned is given in the decision in Thaler v Comptroller General of Patents Trade Marks and Designs (aka ‘Thaler’ or ‘DABUS case’) and in particular in our view in the statements by Lord Justice Birss (L.J. Birss) in his dissenting opinion (See paragraphs numbered 8, 58 78 et seq. of the DABUS case, and the Conclusion).
In summary, L.J. Birss. set out his views on the lower courts’ erroneous interpretations of the law and in conclusion stated:
- The inventor of an invention under the 1977 Act is the person who actually devised the invention.
- Dr Thaler has complied with his obligations under s13(2) of the 1977 Act because he has given a statement identifying the person(s) he believes the inventor to be (s13(2)(a)) and indicating the derivation of his right to be granted the patent (s13(2)(b)).
- It is no part of the Comptroller's functions under the 1977 Act to deem the applications as withdrawn simply because the applicant's statement under s13(2)(a) does not identify any person who is the inventor. Since the statement honestly reflects the applicant's belief, it satisfies s13(2)(a).
- It is no part of the Comptroller's functions under the 1977 Act to in any way be satisfied that the applicant's claim to the right to be granted the patent is good. In granting a patent to an applicant the Comptroller is not ratifying the applicant's claim to derivation. Dr Thaler's asserted claim, if correct, would mean he was entitled to the grant. Therefore the statement satisfies s13(2)(b).
- The fact that the creator of the inventions in this case was a machine is no impediment to patents being granted to this applicant.
All three judges in Thaler agreed that under the Patents Act (PA) 1977 an inventor must be a person, and as a machine is not a person it, therefore, cannot be an "inventor" for the purposes of section 7(2) of the Act. L.J. Birss however dissented on the crucial point whether it was an impediment to the grant of an application that the creator of an invention was a machine, as such. He stated that it was simply that a machine inventor cannot be treated as an inventor for the purpose of granting the application.
In Australia the Court has taken a slightly different view but there, the law is different. As L.J. Birss in Thaler remarked in his judgment:
‘After the hearing the appellant sent the court a copy of the judgment of BeachJ of 30th July 2021 in the Federal Court of Australia Thaler v Commissoner of Patents [2021] FCA 879. The judgment deals with another parallel case about applications for the same inventions. Beach J decided the case in Dr Thaler's favour. However yet again the relevant legislation is quite distinct from that in the UK. The applications reached the Australian Patent Office via the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), which meant that a local rule (reg 3.2C(2)(aa)) applied which requires the applicant to provide the name of the inventor. That rule is in different terms from s13(2) and the present case is not a PCT application ( i.e. in Australia the name of the inventor must be provided unlike under UK legislation). If it were then the operation of s13(2) would be affected by a deeming provision (s89B(1)(c)) which we do not have to consider”.
We believe that in principle LJ Birss is correct and that the patentability of such inventions where created by AI, or with the assistance of AI, provided the basic criteria under the relevant legislation are met, has been established. There is therefore absolutely no need for the patent system to identify AI as the inventor or to create entirely new rights
If the IPO takes the view or on appeal it is established that the law has not been correctly expressed by LJ Birss, it should be clarified to accord with his judgment. Failing that , for instance if AI systems themselves are treated as inventors, in our view, the system of innovation and inventorship in the UK will be eroded, the benefits and incentives for human inventors will be reduced, and ultimately firms could invest more in AI systems than in human innovation.
Without changes in taxes on AI-inventorship and commensurate incentives to balance the negative impact, such a change would be detrimental to the ethos of the patent system and its focus on “a person” being the inventor mentioned in a patent application.
Whilst it is unclear exactly what the future regulation of AI and associated IP rights will look like in the UK at this stage, it is clear however that an internationally harmonised approach to the protection and recognition accorded to AI generated inventions would be desirable.
it is also our view right in principle, to cite L.J. Birss, that ‘there is no rule of law that a new intangible produced by existing tangible property is the property of the owner of the tangible property’, as Dr Thaler contended, and certainly no rule that the property contemplated by section 7(2)(b) in an invention created by a machine is owned by the owner of the machine. Accordingly, the hearing officer and the judge were correct to hold that Dr Thaler is not entitled to apply for patents in respect of the inventions given the premise that DABUS made the inventions’.
In our view, as with AI creations for copyright purposes, the key is the operation and control of the machine/AI producing the invention not ownership of the AI itself.
Ranking Options in order:
- We would therefore urge the IPO to elect Option 1 whereby it is clarified that “Inventor” includes a human responsible for the inventive activity of the AI system that lead to the invention or which devises inventions (e.g. where that humanoperator selects or guides the AI with relevant data, parameters, data-sets or programming logic for the AI’s function or purpose, which leads it to create an invention). This would also cater for the analogous scenario (to that mentioned above under 1, where AI becomes prevalent in the first instance as “AI-as-a-service”, whereupon there should be a presumption of ownership by the AI Operator (not the AI-system owner) and where transfers of ownership and rights can be addressed contractually at the point of use where AI is used ‘…as-a-service’.
- As a second-best option, as requested-particularly if the opinion of LJ Birss is subsequently confirmed by the Supreme Court - we would advocate Option 0 – no change.
Endnotes
- Reference: In Authors Guild v. Google 721 F.3d 132 (2d Cir. 2015), a copyright case heard in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York, and on appeal to the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit between 2005 and 2015. The case concerned fair use in copyright law and the transformation of printed copyrighted books into an online searchable database through scanning and digitization. The case centered on the legality of the Google Book Search (originally named as Google Print) Library Partner project that had been launched in 2003. Though there was general agreement that Google's attempt to digitise books through scanning and computer-aided recognition for searching online was seen as a transformative step for libraries, many authors and publishers had expressed concern that Google had not sought their permission to make scans of the books still under copyright and offered them to users.
- Two separate lawsuits, including one from three authors represented by the Authors Guild and another by Association of American Publishers, were filed in 2005 charging Google with copyright infringement. Google worked with the litigants in both suits to develop a settlement agreement (the Google Book Search Settlement Agreement) that would have allowed it to continue the program though paying out for works it had previously scanned, creating a revenue program for future books that were part of the search engine, and allowing authors and publishers to opt-out. The settlement received much criticism as it also applied to all books worldwide, included works that may have been out of print but still under copyright, and may have violated antitrust aspects given Google's dominant position within the Internet industry. A reworked proposal to address some of these concerns was met with similar criticism, and ultimately the settlement was rejected by 2011, allowing the two lawsuits to be joined for a combined trial. In late 2013, after the class action status was challenged, the District Court granted summary judgement in favour of Google, dismissing the lawsuit and affirming the Google Books project met all legal requirements for fair use. The Second Circuit Court of Appeal upheld the District Court's summary judgement in October 2015, ruling Google's "project provides a public service without violating intellectual property law."[1] The U.S. Supreme Court subsequently denied a petition to hear the case.[2]
A big thank you to Christian for all his hard work on this response.
Lord C-J : Protect Pure Maths
During the Report Stage of the Advanced Research and Invention Agency Bill I spoke in favour of changes to the bill to ensure that pure maths research was included in the definition of scientific research.

This is the recording
https://twitter.com/i/status/1470883981973463049
And this is what I said:
My Lords, I have signed and I support Amendments 12, 13 and 14. As someone immersed in issues relating to AI, machine learning and the application of algorithms to decision-making over the years, I, too, support Protect Pure Maths in its campaign to protect pure maths and advance the mathematical sciences in the UK—and these amendments, tabled by the noble and gallant Lord, Lord Craig, reflect that.
The campaign points out that pure maths has been a great British success story, with Alan Turing, Andrew Wiles and Roger Penrose, the Nobel Prize winner—and, of course, more recently Hannah Fry has popularised mathematics. Stephen Hawking was a great exemplar, too. However, despite its value to society, maths does not always receive the funding and support that it warrants. Giving new funding to AI, for instance, risks overlooking the fundamental importance of maths to technology.
As Protect Pure Maths says, the 2004 BEIS guidelines on research and development, updated in 2010, currently limit the definition of science and research and development for tax purposes to the systematic study of the nature and behaviour of the physical and material universe. We should ensure that the ARIA Bill does not make the same mistake, and that the focus and capacity of the Bill’s provisions also explicitly include the mathematical sciences, including pure maths. Maths needs to be explicitly included as a part of scientific knowledge and research, and I very much hope that the Government accept these amendments.
Lord C-J helps to launch Rolls-Royce Aletheia Framework version 2
The Aletheia Framework is a practical one-page toolkit that guides developers, executives and boards both prior to deploying an AI, and during its use. A second version has been dwveloped by Caroline Gorski and her team at R2 Data Labs, Rolls Royce to be applicable accross a wise range of secotors.
This is how they describe it:
"It asks them to consider 32 facets of social impact, governance and trust and transparency and to provide evidence which can then be used to engage with approvers, stakeholders or auditors.
A new module added in December 2021 is a tried and tested way to identify and help mitigate the risk of bias in training data and AIs. This complements the existing five-step continuous automated checking process, which, if comprehensively applied, tracks the decisions the AI is making to detect bias in service or malfunction and allow human intervention to control and correct it."
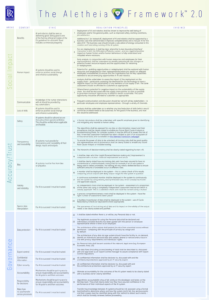
I commented on the original version of The Aletheia Framework, and it deals with many of the same areas in education as it does for Rolls-Royce in manufacturing – ethics, impact, compliance, data protection. So, I saw an equivalence there and the Institute for AI Ethics in Eduction adapted The Aletheia Framework for its needs.
Here are the two videos I made with Rolls Royce to mark the new version:
First on why practical ethics matters right now to build public trust
https://www.rolls-royce.com/sustainability/ethics-and-compliance/the-aletheia-framework.aspx
Second to describe how we adapted the Aletheia Framework for education
https://www.lordclementjones.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Education-case-study.mp4
Launch of AI Landscape Overview: Lord C-J on AI Regulation
It was good to launch the new Artificial Intelligence Industry in the the UK Landscape Overview 2021: Companies, Investors, Influencers and Trends with the authors from Deep Knowledge Analytica nd Big Innovation Centre and my APPG AI Co Chair Stephen Metcalfe MP, Professor Stuart Risssell the Reith lecturer , Charles Kerrigan of CMS and Dr Scott Steedman of the BSI
Here is the full report online
https://mindmaps.innovationeye.com/reports/ai-in-uk
And here is what I said about AI Regulation at the launch:
A little under 5 years ago we started work on the AI Select Committee enquiry that led to our Report AI in the UK: Ready Willing and Able? The Hall/Pesenti Review of 2017 came at around the same time.
Since then many great institutions have played a positive role in the development of ethical AI. Some are newish like the Centre for Data Ethics and Innovation, the AI Council and the Office for AI; others are established regulators such as the ICO, Ofcom, the Financial Conduct Authority and the CMA whichhave put together a new Digital Regulators Cooperation Forum to pool expertise in this field. This role includes sandboxing and input from a variety of expert institutes on areas such as risk assessment, audit data trusts and standards such as the Turing, Open Data, the Ada Lovelace, the OII and the British Standards Institute. Our Intellectual Property Office too is currently grappling with issues relating to IP created by AI .
The publication of National AI strategy this Autumn is a good time to take stock of where we are heading on regulation. We need to be clear above all , as organisations such as techUK are, that regulation is not the enemy of innovation, it can in fact be the stimulus and be the key to gaining and retaining public trust around AI and its adoption so we can realise the benefits and minimise the risks.
I have personally just completed a very intense examination of the Government’s proposals on online safety where many of the concerns derive from the power of the algorithm in targetting messages and amplifying them. The essence of our recommendations revolves around safety by design and risk assessment.
As is evident from the work internationally by the Council of Europe, the OECD, UNESCO, the Global Partnership on AI and the EU with its proposal for an AI Act, in the UK we need to move forward with proposals for a risk based regulatory framework which I hope will be contained in the forthcoming AI Governance White Paper.
Some of the signs are good. The National AI strategy accepts the fact that we need to prepare for AGI and in the National Strategy too they talk too about
- public trust and the need for trustworthy AI,
- that Government should set an example,
- the need for international standards and an ecosystem of AI assurance tools
and in fact the Government have recently produced a set of Transparency Standards for AI in the public sector.
On the other hand
- Despite little appetite in the business or the research communities they are consulting on major changes to the GDPR post Brexit in particular the suggestion that we get rid of Article 22 which is the one bit of the GDPR dealing with a human in the loop and and not requiring firms to have a DPO or DPIAs
- Most recently after a year’s work by the Council of Europe’s Ad Hoc Committee on the elements of a legal framework on AI at the very last minute the Government put in a reservation saying they couldn’t yet support the document going to the Council because more gap analysis was needed despite extensive work on this in the feasibility study
- We also have no settled regulation for intrusive AI technology such as live facial recognition
- Above all It is not yet clear whether they are still wedded to sectoral regulation rather than horizontal
So I hope that when the White Paper does emerge that there is recognition that we need a considerable degree of convergence between ourselves the EU and members of the COE in particular, for the benefit of our developers and cross border business that recognizes that a risk based form of horizontal regulation is required which operationalizes the common ethical values we have all come to accept such as the OECD principles.
Above all this means agreeing on standards for risk and impact assessments alongside tools for audit and continuous monitoring for higher risk applications.That way I believe we can draw the US too into the fold as well.
This of course not to mention the whole Defence and Lethal Autonomous Systems space, the subject of Stuart Russell’s Second Reith Lecture which despite the promise of a Defence AI Strategy is another and much more depressing story!
Report of the Joint Committee on the Online Draft Bill: New offences and tighter rules
After 4 months work the Joint Select Committee on the Draft Online Safety Bill, with Damian Collins MP as our excellent Chair, has produced its report to generally favorable reviews
We have tried to ensure in our recommendations that the safety duties placed on Ofcom and the platforms are much clearer, by reference to existing and new, Law Commission recommended, offences and at the same time we do not infringe rights to freedom of expression. We have also recommended that paid for advertiing and online scams are included in regulated acctivity. We have recommended that it be made clear that all commercial pornography site be subject to the Age Appropriate Design Code aso that Age Assurance ensures that young people are are not subjected to unwanted online porn. We have also recommended that the role of Online Safety Ombudsman be established.
Here is the BBC summary
https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/technology-59638569
And here is the official parlimentary summary
https://ukparliament.shorthandstories.com/draft-online-safety-bill-joint-committee-report/index.html
The online world has revolutionised our lives
While the internet has created many benefits, underlying systems using data harvesting and microtargeted advertising have shaped the way we experience it.
Algorithms, invisible to the public, decide what we see, hear and experience. For some service providers, this means valuing the engagement of users at all costs, regardless of what holds their attention. This can result in amplifying the false over the true, the extreme over the considered, and the harmful over the benign.
The human cost of an unregulated internet can be counted in:
- mass murder in Myanmar
- intensive care beds full of unvaccinated covid-19 patients
- insurrection at the US Capitol
- teenagers sent down rabbit holes of content promoting self-harm, eating disorders and suicide.
The Online Safety Bill is a key step forward for democratic societies to bring accountability and responsibility to the internet.
We want the Bill to be easy to understand for service providers and the public alike. It should have clear objectives that lead into precise duties on the providers, with robust powers for the regulator to act when the platforms fail to meet those legal and regulatory requirements.
Online services should be held accountable for the design and operation of their systems and regulation should be governed by a democratic legislature and an independent Regulator—not Silicon Valley.
Four recommendations to strengthen the Bill
1. What's illegal offline should be regulated online
We agree that the criminal law should be the starting point for regulation of potentially harmful online activity, and that safety by design is critical to reduce its prevalence and reach.
A law aimed at online safety that does not require companies to act on, for example, misogynistic abuse or stirring up hatred against disabled people would not be credible. Leaving such abuse unregulated would itself be deeply damaging to freedom of speech online.
2. Ofcom should issue binding Codes of Practice
We recommend that Ofcom be required to issue a binding Code of Practice to assist providers in identifying, reporting on and acting on illegal content, in addition to those on terrorism and child sexual exploitation and abuse content.
As a public body, Ofcom's Code of Practice will need to comply with human rights legislation and this will provide an additional safeguard for freedom of expression in how providers fulfil this requirement.
3. New criminal offences are needed
We endorse the Law Commission's recommendations for new criminal offences in its reports.
The reports recommend the creation of new offences in relation to a number of harmful online activities.
We recommend that the Government bring in the Law Commission's proposed Communications and Hate Crime offences with the Online Safety Bill, if no faster legislative vehicle can be found. Specific concerns about the drafting of the offences can be addressed by Parliament during their passage.
4. Keep children safe from accessing pornography
All statutory requirements on user-to-user services, for both adults and children, should also apply to Internet Society Services likely to be accessed by children, as defined by the Age Appropriate Design Code. This would have many advantages.
In particular, it would ensure all pornographic websites would have to prevent children from accessing their content. Many such online services present a threat to children both by allowing them access and by hosting illegal videos of extreme content.